Chapter 5-The heyday of home appliances and the dawn of personal computers (Showa50s)

Akihabara station square which is almost the same as the present
(1982: Product names such as “record needle” on the signboard represent those days)
Japan as a whole / Home appliances market in the Showa 50s (economy)
 |
| July 1975 / Sony / VCR Betamax SL-7300 (with TV tuner) / 285,000 yen |
In the 50’s of the Showa era, after the first oil crisis that started in 1973 and the second oil crisis in 1979, and after the energy crisis, we strongly recognized that the resources of the earth are limited, including environmental problems. It was a decade of “saving and energy saving” that shifted to low growth.
The word “era of uncertainty” was spoken, and it was a ten-year slump in the world, including the arrest of former Prime Minister Tanaka in the Lockheed scandal and the retirement of superstars such as Nagashima and Wang. On the other hand, looking only at the consumer electronics industry, in the early Showa 50s, spending on durable consumer goods increased by an average of 6.7% (1975-1978) annually, an increase of 1.4% from the average consumer spending during the same period. It has grown significantly compared to.
 |
| October 1976 / Victor / VTR / HR3300 (VHS No. 1) / 256,000 yen |
The reasons for this are: 1) While prices have risen through the energy crisis, home appliances have been called “price honor students” and their prices have stabilized, giving them a sense of cheapness. 2) The replacement demand for products with a high penetration rate has become apparent due to the refraining from buying due to the oil crisis of 1973-1974. 3) Room cooler (penetration rate: 1976 19.5% → 1984 49.3%) Futon dryer (penetration rate: 1978 6.2% → 1984 18.7%) Video (penetration rate: 1978 1.3% → 1984) 18.7% a year) and new products were born. 4) System components and radio cassette recorders that began to sell explosively around 1975, “Walkman” that was released in 1979 and influenced the world music culture, or washing machines and refrigerators that were only white in the past have been colored. , A new product that reflects the lifestyle of young people and new families was born, and pulled the home appliance market.
 |
| 1978 / Matsushita / Color TV / TH-20-B8 / Panacolor Unit 1 / 218,000 yen |
In 1978, the “Invaders game” became an explosive trend, and with the success of YMO, an electronic sound of “picopico” was heard all over the city. It will make a start to the current prosperity of the game market.
In 1982, a new media boom occurred, and Captain CATV attracted attention along with microcomputers, but it was not enough to significantly change society, and it will spend the era of sexual intercourse until the present multimedia era.
In 1983, the annual production of video exceeded that of color TVs, leading to the explosive hit of AV and large-screen TVs in the Showa 60s.
On the other hand, with the progress of motorization in Japan, the annual domestic sales of automobiles will exceed 5 million units, and more than one car will become widespread in the family. With the development of the food service industry that landed with Kentucky Fried Chicken in 1970, McDonald’s and Mister Donut in 1971, and Denny’s in 1974, the chain store system began to show rapid growth in the suburbs, and shopping centers began to appear on the suburban roadside. It is also in the Showa 50s.
Akihabara’s Showa 50s (Part 1-Completed cityscape)
 |
| March 1979 / Sanyo / Mini stereo cassette recorder / MR-U4 / 43,800 yen |
From 1971 to 1972, the development boom in Japan based on the “Remodeling of the Japanese Islands” advocated by Prime Minister Kakuei Tanaka caused land prices to soar, and since 1970, Akihabara and other commercial clusters throughout Japan have soared. In order to increase the productivity of the land, we built a high-rise building and worked to expand the commercial space. In Akihabara, after the remaining two-thirds of the Radiokaikan was completed in May 1972, skyscrapers lined up one after another, and the current cityscape was almost completed in the early Showa 50s. In addition, the area called “Akihabara” began to expand, and retailers, wholesalers, and manufacturers centered on parts dealers were born around Kanda-ji Temple from the back of Nippon Express. Around the same time as the opening of the Washington Hotel, the New Chiyoda Building was built, and Dai-Ichi Katei Denki, Maruzen Denki Electric built the building, transforming this area into a “microcomputer / personal computer” area. On the Showa-dori side, parts trading companies focusing on exports were also established one after another.
With the expansion of the sales area and the appearance of attractive home appliances, Akihabara’s “growth myth” continued even in the Showa 50s, almost unaffected by the oil crisis.
Akihabara’s Showa 50s (Part 2-Birth of microcomputers and electronic components)
 |
| July 1979 / Sony / Walkman / TPS-L2 / 33,000 yen |
In 1977, when the 8-bit personal computer Apple was released in the United States and 16-bit microprocessors such as the Intel 8086 appeared, the number of stores handling computers began to increase in Akihabara around 1979. As the transistor changed to IC and LSI, Akihabara began to have a face as the center of electronic components.
The first microcomputer shop in Japan opened “NEC Bit INN Tokyo” on the 2nd floor of Radiokaikan in 1976. In addition to the hall, new areas such as Mahikari Radio’s all-microcomputer building (New Chiyoda Building), Rocket Main Store’s microcomputer section, and Tanaka Electric’s Toshiba PC floor have expanded along the Kanda River.
In 1982, six stores, including Sato Musen, opened in a month, and from 1982 to 1983, the microcomputer business, which was once treated as a maverick, was finally recognized.
 |
| February 1984 / Sharp / Word processor WD500 / 330,000 yen |
Also, junk shops have begun to be born. International Radio opened a junk shop behind Hirose Musen in 1973, and Akizuki Denshi opened a junk shop behind Hirose Musen in 1974, and it was in the Showa 50s that the junk shop, another face of Akihabara, grew.
Many of the businessmen who are active in the current personal computer / multimedia industry must remember hitting the keyboard at each microcomputer shop in Akihabara during this period. Indeed, the sprouting of the current multimedia society was in Akihabara in the Showa 50s.
Akihabara in the Showa 50s (Part 3-Rapid internationalization)
 |
| 1979 / Pioneer / System Component Pioneer A7 |
Since the 1965’s, when the technological capabilities of Japanese manufacturers have caught up with the world, Japanese home appliances have become popular all over the world. “Made in Japan” has become an era of proof of quality, and foreigners visiting Japan for sightseeing and business should shop in Akihabara to buy Japanese home appliances (radio, Walkman, stereo, etc.) as souvenirs. became.
For such customers, the number of shops with “duty free shops” has increased in Akihabara, and around 1982, about 15 shops such as Laox, Hirose Musen, Yamagiwa, Nishikawa Musen, Onoden, and Yamamoto Musen have duty-free shops and duty-free floors. Was provided.
 |
| April 1980 / Toshiba / washing machine / dryer / dedicated stand set / SD-200N / ED-700N / DS-60N / 52,000 yen |
Originally, Akihabara was a lively town with signs and lights of manufacturers and stores, unique signs and pops of store displays, but announcements and signs for foreigners, or foreign clerk at the store. The number of people has increased, and it has become an increasingly stateless and mysterious space.
With the success of Japanese home appliance makers all over the world, “AKIHABARA” has become a world-famous city.
 |
| 1980 / Matsushita / VTR / NV-3000, VZ-C650N (camera) / 198,000 yen / 138,000 yen |
Akihabara’s Showa 50s (Part 4-Establishment of Akihabara Electric Town Promotion Association)
The following year, the “Akihabara Electric Festival” was held from 1980, and the largest campaign (estimated) in a single shopping district continues to this day.
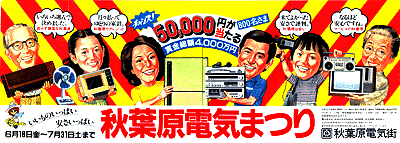
1982 Akihabara Electric Festival
A poster for the “Akihabara Electric Festival”, which is the second year since the start. Large-scale behavior with a total of 40 million yen, where 50,000 yen is equivalent to 800 people.
“A lot of good things, a lot of cheapness” is still the same!

1984 Akihabara Electric Festival
A poster for the “Akihabara Electric Festival”, which is the 4th year since the start. The total prize money is 60 million yen.
The characters are Edison Cleopatra Beethoven DaVinci from the left.
In each poster, the illustrated product was a hit product that I longed for at the time.
